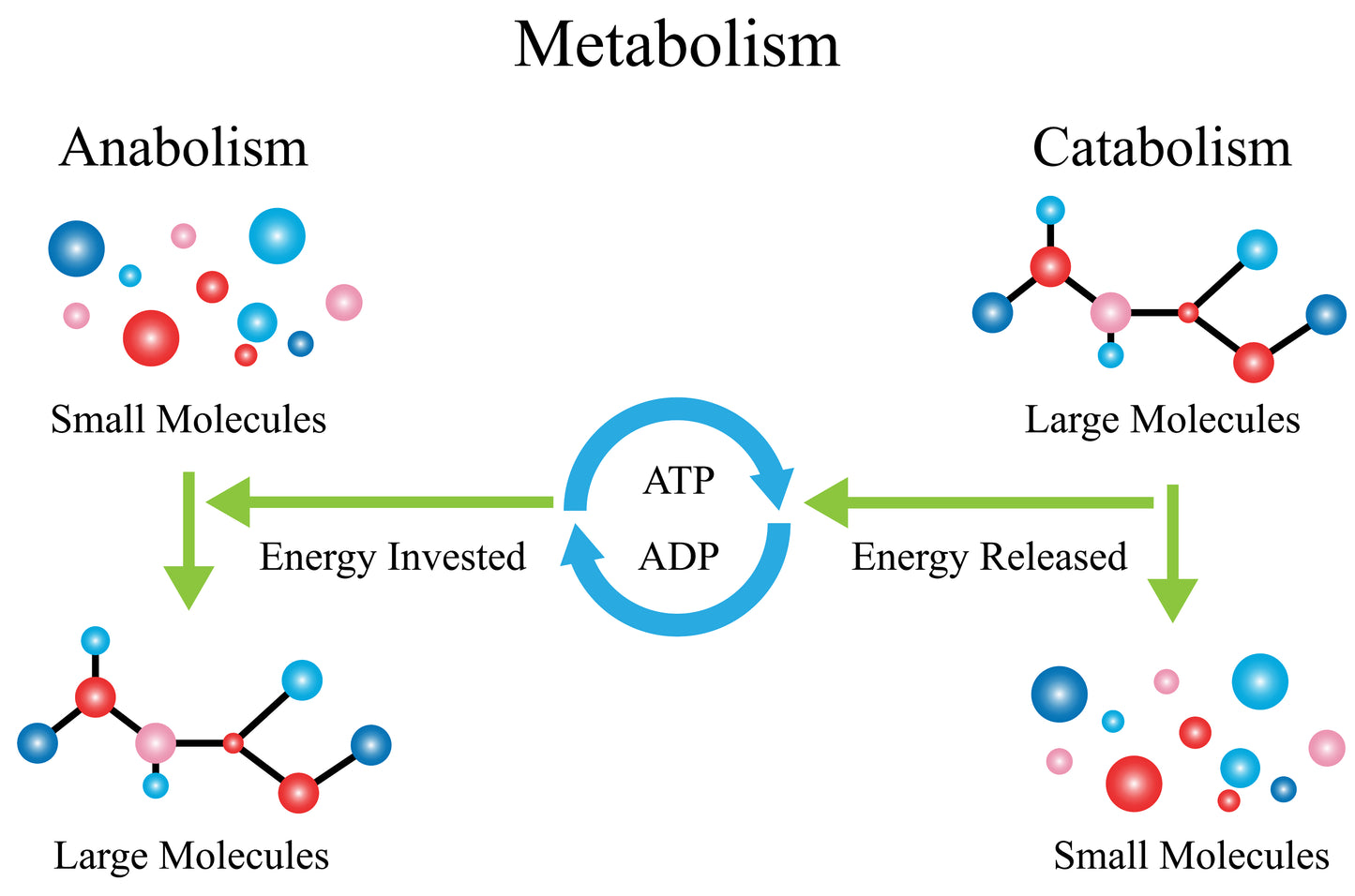
What is Metabolism?
Metabolism according to Jones and Bartlett (n.d.) a general term that encompasses all chemical changes occurring in living organisms that allow us to maintain life. There are two main categories of metabolism, catabolism and anabolism. These two functions fall under metabolic pathways, within are a series of chemical reactions that either break down a large compound into smaller units (catabolism) or synthesize more complex molecules from small ones (anabolism). Jones and Bartlett further include the functions of metabolism.
How catabolism works - Once the bigger molecules have been broken down smaller they are easier to be absorbed and able to be released as energy. For example, when food such as bread (made of 2 molecules is broken down into one (glucose), cells can further catabolise these units into energy. Catabolic processes are proteins becoming amino acids, glycogen into glucose and triglycerides breaking up into fatty acids. This metabolic pathway allows us to use potential energy into kinetic energy in our daily activities.
How anabolism works- The anabolic process is the complete opposite of catabolism as it uses simpler molecules to create complex molecules, and are then stored around the body. An example of how this would look is, when we wake up in the morning our body has already broken down our foods (catabolism) and is now using stored complex molecules so when our muscles contract we catabolise stored molecules and release energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) , therefore allowing us to move and operate our body. This metabolic pathway is also required for maintenance, growth, repair and storage.
Metabolism and weight gain
Metabolism can have a wide range of factors that can influence weight gain. We must first understand our body by evaluating basal metabolic rate (BMR). Using the Harris-Benedict formula which takes into account height, weight, age and gender. This evaluation will determine how many calories we should be consuming, if our current diet is exceeding our recommended intake we may see an increase in weight thus affecting metabolism. You can go online and use a generated BMR calculator which will give you an idea of how much energy you should be consuming,
Metabolism and weight loss
We can look to improve our metabolism in order to promote healthy weight loss. ADL (n.d.) mentions that there are multiple factors that can improve/increase our metabolism:
Activity level- by increasing our activity level we will increase metabolism. When the body is under high intensity exercise it promotes the production rate of both catabolic and anabolic pathways as the body requires kinetic energy, as well as reserved. This will then promote weight-loss which will further increase the rate of metabolism.
Weight loss and healthy eating - healthy weight loss will promote metabolism as eating a healthy balanced diet that are nutrient dense means that we are able to break down the foods easier as the molecules that are made up of protein, fat, and carbs are easily digestible. Our main source of starch will be polysaccharides in addition to the foods being rich in fibre therefore helping with the process of digestion.
Psychological response on metabolism
A psychological reason to help weight loss and metabolism can be to reduce stress. ADL (n.d.) states that stress can release the hormone response of cortisol. Mancella.G (2020) includes cortisol can slow down metabolism, and explains that cortisol can cause cravings to fatty, sweet, and salty foods, causing over indulging in less nutritious meals. To further include cortisol has the benefit of maintaining homeostasis in fight or flight situations to keep blood glucose levels under control.
Risks on dropping weight too quickly
Taking the following strategies, or any strategies in that fact to increase metabolism with the goal to lose weight, ADL (n.d) we must take in consideration that losing a large amount of weight quickly has consequences. Losing a significant amount of weight too quickly can cause the release of toxins into the bloodstream from our fat cells, which cannot be effectively detoxified by the liver or kidney causing reduction in energy production meaning that we could potentially hit a wall and go backwards and lead to weight gain. We need to consider the fact that this is about making a lifestyle change "life" meaning longevity, we do not want to rush and cause further harm.
Taking all that in consideration we hope you come away with a lot of info on how metabolism works. We advise that you seek professional help if you have underline health conditions that could be causing weight gain as prescription medicine can play a big factor on the rate of metabolism. Speak to your doctor in helping you make the adequate changes that will support your dietary needs.
References:
Jones and Bartlett. (n.d). Metabolism. Unknown: Jones and Bartlett publishing. Available at: http://samples.jbpub.com/9780763776633/76633_ch07_5589.pdf
Gabrielle Mancelle (2020). How too much stress can cause weight gain. USA: Orlando Health. Available at: https://www.orlandohealth.com/content-hub/how-too-much-stress-can-cause-weight-gain-and-what-to-do-about-it
Sop ADL. (n.d.) Nutrition For Weight Loss. Metabolism. ADL.
